What is a septic tank and how does it work?
The first septic tank was invented in 1860. Jean-Louis Mouras was determined to create a waste management system that did not involve manual dumping of wastewater. Inspired by flush toilets from ancient Greece and Rome, he developed a sealed tank to collect waste as it leaves the house. He combined his invention with a manure pit, a container that slowly leaks the contents into the surrounding soil. He used his invention for almost a decade without any problems. His invention eventually caught on in the United States, where other entrepreneurs took advantage of his ideas and improved upon his designs. Today, septic tanks are a popular solution for waste management in rural homes and are effective at filtering waste as it enters the soil. Below you can find information about what is a septic tank, how does it work?
What is a septic tank?
A septic tank is a landfill container that is part of a waste removal system for homes and is not connected to the sewer system. They work in conjunction with a drain and a series of pipes to remove waste from the home. After initial and installation costs, maintenance costs for septic systems are very low when they are properly installed. The highest quality and most expensive tanks are made of concrete, but they can also be made of fiberglass and polyethylene.
How does a septic tank work?
A septic tank is a watertight container that receives all the water that comes out of the house. When the waste is collected in the septic tank, it separates into 3 layers: scum, sewage and sludge.
- Scum is the top layer of waste in the tank. It consists of oils and fats that float to the surface of the water. Scum is a by-product of cooking grease, soaps, and other fats that can come from cleaning or hand washing products.
- Wastewater is the middle layer of waste consisting of water left over after scum floats to the top and sludge settles to the bottom of the tank. The wastewater is pumped through the outlet of the tank into the drainage field, where it is dispersed into the soil.
- Sludge is the bottom layer of the sump. It consists of solid waste that sinks to the bottom of the tank as it separates from the water. Sludge also includes by-products of other wastes that break down in the tank.
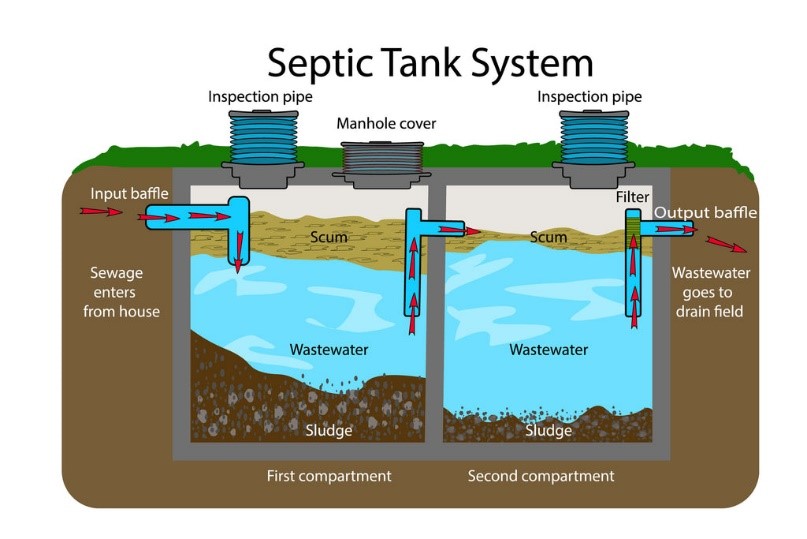
Septic tanks rely on bacteria to break down solid waste that settles to the bottom. After the solids are broken down into liquids, they are pumped out into the drain. Field drainage works in conjunction with septic tanks. Waste containing enough liquid to pump out of the tank is poured into the soil through the drain line.
Problems can arise if the sludge layer of the tank becomes too high. This can clog the drain line and prevent water from escaping. When this happens, puddles will form in your yard.
Septic tanks are usually made of concrete, fiberglass or polyethylene. These materials are ideal because they do not crack easily while underground. If the septic tank cracks, the waste will leak out and form a puddle on the surface above the tank. Septic tanks hold wastewater long enough to separate solids and oils.
What are the parts of a septic system?
A septic system collects all wastewater from a home, decomposes it, and treats it. The following components work together to keep the septic system working:
- Sewer line
- Septic tank
- Sewer
- Drain box
- Soil
Drains
All plumbing in the house leads to the drain line. Then, the drain line brings all the wastewater from the house into the septic tank.
Septic tank
The septic tank receives wastewater from the sewer line. Once in the tank, the liquid waste will pump into the drain line. Solid waste settles to the bottom of the tank as sludge. Natural bacteria will eventually break down the sludge so that it can be pumped into the drainage area.
Sewer
The drainage field, also known as the filter field, receives the liquid waste from the outlet of the tank and disperses it into the soil. Drains consist of downward-sloping underground gravel and pipes to convey wastewater from the septic tank. The arrangement of the parts of the drainage system is designed to prevent sewage from reaching the surface of your yard and to prevent water from overflowing.
Drain box
The distribution box is a concrete or plastic cube designed to distribute wastewater evenly between a drainage zone or a series of drainage zones. It contains multiple drains to different sections of the drain. The distribution box is located lower than the septic tank and uses gravity to receive the wastewater from the tank and distribute the wastewater to the drainage field.
Soil
Soil is an important part of a septic system as it is the final treatment step for wastewater. As water enters the drainage field and seeps down, the soil removes bacteria, viruses, and nutrients in the waste. Not all types of soil are effective in treating septic tank waste. Humus, soil that comes in a variety of particle sizes, is the best soil for a septic system because they don’t clog easily. Soils that absorb water, such as clay and silt, absorb water and are prone to clogging.
Advantages of septic system
There are many upsides to owning a home with a septic system.
- Environmentally friendly septic system
- Septic tanks can last for decades. The lifespan of a septic system ranges from 15 to 40 years depending on how well it is installed and maintained.
- Unless your tank is having problems, they are more cost effective than using a drainage system.
Disadvantages of septic system
While septic tanks are excellent waste removal systems, a number of problems can arise that cause them to not function correctly. The following are common causes of problems in septic tanks:
No regular maintenance
Without maintenance, your tank can become clogged or cracked. If the sludge layer at the bottom of the tank becomes too high, it can clog the drain and clog the drains in your home. Septic tanks typically require emptying every 3 to 5 years. Some tanks may need to be emptied more or less often depending on the number of people living in the home. You can tell if your septic tank is too full if the drainage is backing up or running slower than usual, there is a puddle of water above the septic tank, or if you notice a bad smell coming from the septic tank. You can learn more about how to maintain your septic system on our blog.
They can be damaged by plant roots
Roots can enter the septic pipe if they grow near the tank. If your driveway is cracked, you notice puddles in your yard, or your drains are filled up, tree roots may have punctured your pipes. New plastic septic pipes can withstand pressure from plant roots and will prevent them from becoming a problem. If you plan to plant new trees, make sure you keep the proper distance between them and your septic system.
May overflow
Choosing too small a tank size can cause the tank to overflow if the amount of water used exceeds the tank’s capacity. In general, you should use a tank that is 400 gallons larger than your household uses in a day. If you use 300 gallons of water per day, you should invest in at least a 700 gallon tank. If you install the tank too small, it will overflow and cause puddles in your yard. If you regularly host guests or have large parties, you will want to purchase a tank much larger than your family’s daily use.
May break due to ground movement
Ground movement can put pressure on the tank and cause structural damage. A slight change in the area around your tank can crack the outside of the tank. If your tank is cracked, it will leak sewage and cause puddles on your lawn.
See also: How to diagnose a faulty water meter
Follow Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/SongPhungthietbinganhnuoc/ to update new products
Translator: Duong Nguyen Hoang Khang













